Step 3 – NBME 7 – Block 1
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
A randomized controlled trial is conducted to investigate the efficacy of drug X for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. The study enrolled 200 patients, who were randomized into two groups (Group A and Group B); Group A received treatment with drug X and Group B received treatment with levofloxacin. Characteristics of the study participants in each group are shown:
Characteristic
Group A
Group B
P-value
Age, median years
59
55
.34
Women, %
50.0
51.0
.52
Race/ethnicity, %
.23
White, non-Hispanic
88.5
90.3
Black, non-Hispanic
7.6
6.0
Hispanic
3.1
3.1
Comorbid illness, %
Renal disease
4.1
2.1
.04
Congestive heart failure
3.2
5.1
.08
Liver disease
1.1
0.7
.66
Cerebrovascular disease
0.4
0.3
.50
Hospitalized, %
52
48
.52
The study data show that symptom duration in patients treated with drug X is 10.2 days (standard deviation=4.1 days), compared with 12.8 days (standard deviation=5.2 days) for patients treated with levofloxacin (P=.02). Based on these data, which of the following is the most reasonable statement about drug X for the hospitalized patients?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
A 62-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital because of a 2-day history of fever and a 1-month history of increasing abdominal distention, insomnia, and daytime somnolence. Medical history is unremarkable and she takes no medications. She does not smoke cigarettes or use illicit drugs. She drinks one pint of vodka daily. Her temperature is 38.4°C (101.2°F), pulse is 92/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 112/64 mm Hg. She is alert and fully oriented but appears uncomfortable. Examination shows spider angiomata over the chest. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdominal examination shows distention and flank fullness with a fluid wave and shifting dullness to percussion. Collateral veins are visible around the umbilicus. Examination of the upper extremities shows palmar erythema and asterixis. There is 2+ pitting edema to the knees. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
A 78-year-old man comes to the office because of a 3-week history of severe pain in his left groin with weight-bearing. He has not had any recent falls or other trauma. The patient has a history of prostate cancer treated with seed implant therapy 14 months ago. He receives leuprolide acetate injections monthly. Medical history is also significant for long-standing osteoarthritis in both hips, but the patient notes that his current pain is more severe than his long-standing arthritic pain. BMI is 27 kg/m2. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination discloses tenderness to palpation over the left groin. No inguinal masses are palpated on the left. Range of motion of both hips is full. Plain x-ray of the pelvis and hips shows a fracture of the left superior pubic ramus. Which of the following is the most appropriate study to further evaluate this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
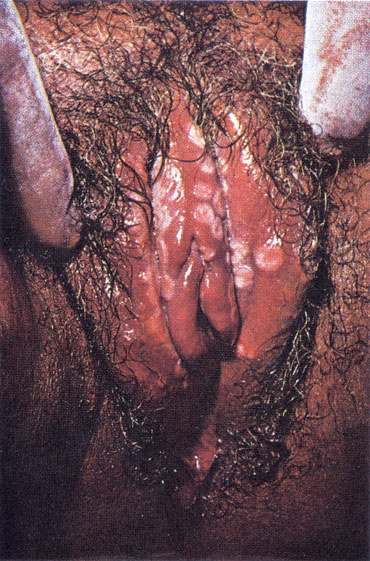
A 26-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of severe vulvar pain and burning. She is 35 weeks pregnant. The pregnancy has progressed without any complications and the fetus has grown appropriately. She has no past history of medical or surgical problems. Vital signs are normal. The patient reports appropriate fetal movements. On pelvic examination her external genitalia appears as shown in the photograph. On further questioning she reports that she has never had this before and that her husband has no symptoms. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
The leadership team at a physical rehabilitation facility learns that a physician at the facility has engaged in sexual activity with a patient. A confidential ad hoc committee is formed to investigate the situation and discovers that the physician also has had sexual contact with two other patients. The physician is interviewed and reports alcohol use disorder and suicidal ideation because his wife recently filed for divorce. He also says that he has been having financial difficulties. The physician apologizes for his “temporary lapse in professionalism.” He accepts immediate referral to an employee assistance program. A confidential root-cause analysis (RCA) is initiated to investigate sexual behavior in the facility, including that between patients and staff. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step regarding reporting this physician’s behavior to the state medical board?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
A 72-year-old woman who resides in a nursing care facility is brought to the emergency department by ambulance 15 minutes after she was found unconscious on the floor of her room. Medical history includes hypertension and atrial fibrillation. She had a cerebral infarction 6 years ago, and she has no residual deficits. Current medications are atenolol and apixaban. On arrival, the patient is unresponsive to verbal stimuli. Temperature is 39.2°C (102.5°F), pulse is 109/min and irregular, respirations are 27/min, and blood pressure is 69/45 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 92%. Physical examination shows that the lungs are clear and the extremities are warm. Which of the following mechanisms best explains the blood pressure measurement in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
A 3-day-old term newborn is admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) of the hospital because of a 12-hour history of poor feeding and respiratory distress. Pregnancy and delivery were uncomplicated; she was delivered vaginally. Apgar score was 8 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. Vital signs in the ICU are temperature 36.2°C (97.1°F), pulse 190/min, respirations 80/min with grunting, and blood pressure 50/25 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 83%. Chest x-ray shows cardiomegaly; echocardiography discloses absence of the mitral valve and aortic root, a large right atrium and right ventricle, and an intact tricuspid valve. Physical examination is most likely to show which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
A randomized, double-blind clinical trial is conducted to determine the efficacy of medical cannabis for improvement of multiple sclerosis (MS) symptoms. A total of 250 patients with MS between the ages of 18 and 65 years who attend a specialized MS neurology clinic are enrolled in the study. One hundred twenty five patients receive capsules containing cannabis extract plus standard pharmacotherapy and 125 patients receive capsules containing standard pharmacotherapy only; all capsules appear identical. All patients provide monthly urine samples to confirm treatment compliance during the 6-month study period. Patients also rate their daily MS symptoms on a 10-point scale, and these data are collected monthly. A composite score is created at the end of the study, with higher scores indicating worsening of symptoms. All patients are analyzed according to their initial group assignment. Results are shown:
Standard Pharmacotherapy
Plus Cannabis Group, %
Standard Pharmacotherapy
Only Group, %
Patients reporting monthly symptoms
85
68
Patients providing monthly urine samples
78
62
Mean composite score (± standard deviation); (P<.001)
6.3 (±1.2)
8.9 (±1.5)
Which of the following is the greatest threat to the validity of this study?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
A 92-year-old man is brought to the office by his 70-year-old daughter because of a 1-week history of rectal bleeding. The patient says he began to experience increasing constipation and noticed “blood in the toilet water.” He has had no changes in his appetite and has not lost any weight. Current medications include daily aspirin and a multivitamin. The patient lives alone. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 87/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 90/72 mm Hg. Rectal examination shows an irregular mass 5 cm from the anal verge. The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. In addition to fluid resuscitation, which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
A 62-year-old man with two unresectable tumors of the liver comes to the clinic to discuss results of an abdominal CT scan obtained 2 days ago. During the past 3 months, he has received leucovorin, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin therapy to shrink the tumors to a potentially resectable size. He has tolerated the therapy well. Vital signs are normal. Examination shows jaundice. The liver border is firm and irregular and the span measures 14 cm by palpation. There is 2+ pedal edema bilaterally. The abdominal CT scan shows that the size of the tumors has not changed. When the patient is told this information, he becomes tearful and looks at the floor silently. Which of the following is the most appropriate empathic statement for this physician to make?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
A 56-year-old man comes to the office because of a 6-week history of increasing urinary frequency and thirst. During this time, he has been urinating large volumes throughout the day and has felt tired. He has not had pain on urination or blood in his urine. Medical history is unremarkable and the patient takes no medications. He drinks 12 beers daily. He does not smoke cigarettes. BMI is 32 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 98/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 118/76 mm Hg. Physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Results of fasting laboratory studies are shown:
Serum
Blood
Urea nitrogen
18 mg/dL
Hemoglobin A1c
12.0%
Creatinine
1.7 mg/dL
Na+
140 mEq/L
K+
4.0 mEq/L
Cl–
100 mEq/L
HCO3−
25 mEq/L
Glucose
272 mg/dL
Urine dipstick shows large ketones. In addition to lifestyle modifications, which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
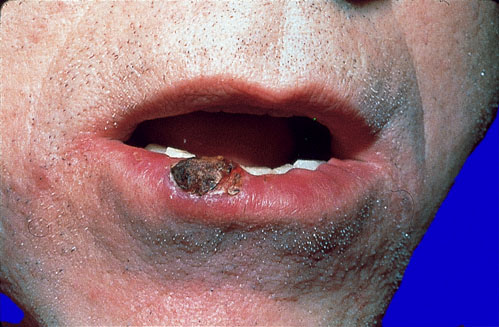
A 68-year-old man comes to the clinic because of a sore on his lower lip that began as an irritation 1 month ago and has progressed to an intermittently painful lesion with drainage. The patient’s ability to eat and drink has not been affected. He has noticed no other skin lesions and notes no other symptoms. Medical history is significant for prostate cancer and hypertension. His only medication is chlorthalidone. He is a retired construction worker. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 50 years. He has been sexually active with multiple partners and does not use condoms. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 82/min, respirations 12/min, and blood pressure 132/78 mm Hg. Physical examination discloses the findings shown in the photograph. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
A 93-year-old woman comes to the office as a new patient. She feels well. She has hyperlipidemia treated with atorvastatin. She has no other history of serious illness and takes no other medications. Her last colonoscopy 25 years ago and her last mammography and DEXA scan 30 years ago showed no abnormalities. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows no abnormalities. The patient asks what preventive health measures she should take. Which of the following is the most appropriate physician response?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
A researcher is investigating the rate of type 2 diabetes mellitus among residents of a town in the midwestern United States. A total of 10,000 people live in the town, and 400 of these residents have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Over the next 6 months, an additional 100 residents are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. There has been no migration of people into or out of the town during this period of time. Based on this information, which of the following best represents the annualized incidence rate of type 2 diabetes mellitus in this town?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 2 items.
A 25-year-old Laotian woman has just given birth to her first child. Her prenatal laboratory studies indicate that she is positive for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). She denies a recent infection or known exposure and states that she immigrated to the USA 8 years ago. Physical examination of the newborn shows no abnormalities.
Item 1 of 2
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the care of the newborn?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
Item 2 of 2
When you counsel the parents regarding neonatal care, they should be informed of which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
A 73-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 2-day history of severe low back pain that began after she lifted her grandchild out of his crib. She rates the pain as an 8 on a 10-point scale and says it radiates to the abdomen. The pain worsens when she sits down and when she flexes or twists her back; it improves when she lies flat on her back. Ibuprofen and heating pads have provided modest improvement of the pain. Medical history is significant for hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide, and asthma treated with inhaled fluticasone and albuterol. Family history is significant for osteoarthritis in her sister and breast cancer in her mother. The patient drinks two glasses of wine daily and has smoked one-half pack of cigarettes daily for the past 50 years. Vital signs are temperature 37.2°C (99.0°F), pulse 94/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 168/94 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 91%. The patient has a great deal of difficulty getting herself onto the examination table because of her back pain. Auscultation of the chest discloses end-expiratory wheezing. There is tenderness to palpation posterior to L1–L2. Straight-leg raising does not markedly increase the back pain. Neurologic examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic study?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
A 75-year-old retired accountant is admitted to the hospital for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. He initially was seen in the emergency department. He was treated with intravenous fluids and antibiotics. In the hospital, his daughter, who accompanies him, says he has seemed depressed recently. The patient has lived alone and has been self-sufficient since his wife died 2 years ago. Medical history is remarkable for hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Preadmission medications included lisinopril, which was discontinued by the patient. The patient has not seen a physician during the past 8 months. BMI is 18 kg/m2. The daughter notes that his weight is 7 kg (15 lb) less than his weight 6 months ago. Vital signs are temperature 37.7°C (99.9°F), pulse 98/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 110/70 mm Hg. Oral examination shows mild glossitis. There is mild lateral nystagmus and bilateral paralysis of the lateral gaze. Neurologic examination discloses no other abnormalities. Chest x-ray shows consolidation of the middle lobe of the right lung. Results of laboratory studies are pending. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s ophthalmologic findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
A 19-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 3-hour history of left lower abdominal pain that began when he felt as if he pulled a muscle while playing soccer. The patient says he has had similar episodes of pain in the past, but they resolved spontaneously. Medical history is unremarkable and he takes no medications. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 118/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 122/78 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 99%. Abdominal examination discloses normoactive bowel sounds and mild voluntary guarding of the left lower quadrant. The left scrotum is swollen and tender. Which of the following physical examination techniques is most critical to complete in order to assess the need for emergent consultation with a urologist?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
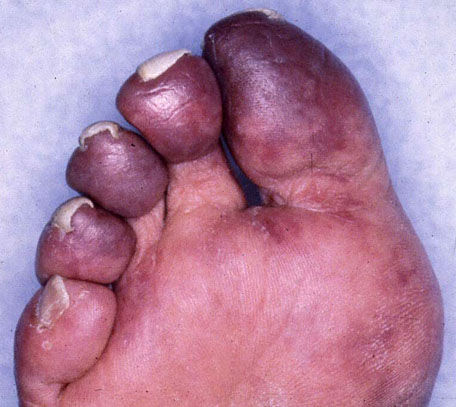
A 70-year-old man is evaluated in the hospital 24 hours after being admitted for a non–ST elevation myocardial infarction. The patient underwent cardiac catheterization and placement of a drug-eluting stent in his left circumflex coronary artery. Medical history also is remarkable for hyperlipidemia and hypertension. Medications are clopidogrel, lisinopril, metoprolol, rosuvastatin, and 325-mg aspirin. Temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse is 68/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 155/90 mm Hg. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination discloses a regular rhythm without murmur. No edema is noted in the lower extremities. Pedal pulses are palpable. The toes on both feet appear as shown in the photograph. Based on these findings, the patient is at greatest risk for which of the following additional complications?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
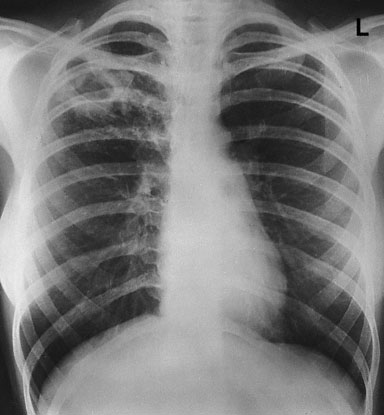
A 58-year-old woman comes to the office because of cough productive of greenish sputum for the past 2 months. She has not noted blood in the sputum. She says, “Sometimes I think I have a fever, but I haven’t bothered to take my temperature.” Her husband thinks she may have lost a few pounds. She says she has been too busy to eat. No one else at home is sick. Medical history is unremarkable and the patient takes no medications. She has had the normal childhood vaccinations but has not received the pneumococcal or influenza vaccines. She had smoked one-half pack of cigarettes daily for 15 years but quit 20 years ago. She drinks two to three glasses of wine on the weekends. Her husband is her only sexual partner. She works as a nurse in a large city hospital. Her parents died in their 90s of natural causes. Vital signs are temperature 37.8°C (100.0°F), pulse 80/min, respirations 14/min, and blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg. Physical examination discloses no abnormalities except for the cough. Chest x-ray is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
A 45-year-old woman is being prepared to undergo ileoscopy to assess the activity of her Crohn disease. Because of severe fistula formation, the patient has undergone both ileostomy and a diverting bilateral ureterostomy in the past, both of which were diverted to the anterior abdominal wall. The patient is brought to the operating room and draped; the abdominal wall is exposed. When the gastroenterologist enters the operating room, he performs a time out indicating the patient’s name and date of birth, his own name, and the planned procedure. He picks up the colonoscope, but as he approaches the patient, he realizes he is not aware which of the ostomies connects to the ileum internally and aborts the procedure to obtain further information before proceeding. Which of the following strategies did the endoscopist use in order to protect this patient’s safety?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 3 items.
A 6-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by the school nurse after an eye injury. The boy was jumping down the stairs when he slipped and fell forward. He was carrying a pencil at the time and was struck in the right eyelid by the pencil point. He is complaining of pain over the right eye. The child sustained no other injuries. The patient’s parents could not be reached. Physical examination of the child shows a healthy boy who is tearful but who is in no acute distress. There is a 1/4-inch laceration involving the center of the right upper lid. He resists attempts to open his eyes. With difficulty, you examine the eyes and find that the pupils are equal and react normally to light. There is no injection of the bulbar conjunctiva. No foreign body is seen.
Item 1 of 3
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
Item 2 of 3
The diagnosis that would have the most significant impact on this patient’s prognosis is which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
Item 3 of 3
The school nurse, who has accompanied the patient, asks you to delay further management or disposition until a parent can be contacted to sign consent for the patient’s further care. Which of the following is the most appropriate response to the school nurse?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
An 18-year-old male college student comes to the student health center because of a 24-hour history of a generalized, sharp, pounding headache that developed abruptly. During this time, he also has had nausea, loose stools, palpitations, and sweating. He has had three to four episodes of similar symptoms during the past month. Medical history is unremarkable and he takes no medications. Vaccinations are up-to-date. The patient does not smoke cigarettes, drink alcoholic beverages, or use illicit drugs. BMI is 19 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 38.1°C (100.5°F), pulse 120/min, respirations 24/min, and blood pressure 182/110 mm Hg. The patient appears to be anxious and in distress. Skin is pale, warm, and moist. Cardiac examination discloses tachycardia and a hyperactive precordium. Abdomen is soft and nontender; no masses are palpated. Neurologic examination discloses a fine tremor of the hands. Results of laboratory studies disclose increased urine catecholamine concentrations. Subsequent CT scan of the abdomen and 123I-MIBG scintigraphy confirm the diagnosis. Surgical intervention is arranged. Which of the following is the most appropriate preoperative pharmacotherapy for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 2-day history of malaise, nausea, and vomiting. Ten days ago, he was discharged from an acute rehabilitation facility, where he had resided for 6 weeks while recovering from multiple rib fractures, a ruptured spleen, and bilateral femur fractures sustained in a motor vehicle collision. Treatment after the collision consisted of exploratory laparotomy, splenectomy, bilateral femur repair, and respiratory and pain management. He received five units of packed red blood cells during his hospitalization, and on discharge he was given a pneumococcal vaccination. Since discharge from the acute rehabilitation facility he has not been sleeping or eating well and has had little urine output. Medical history otherwise is unremarkable. Medications are acetaminophen-oxycodone taken every 2 to 3 hours for pain and over-the-counter analgesics as needed. BMI is 25 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.4°C (99.4°F), pulse 120/min, respirations 20/min, and blood pressure 90/70 mm Hg. The patient appears ill. Physical examination shows mild jaundice. Abdominal examination shows a well-healed surgical incision with no sign of infection; there is tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant. X-ray of the abdomen shows no abnormalities. Results of laboratory studies are shown:
Serum
Blood
ALT
330 U/L
Hematocrit
30%
AST
420 U/L
Hemoglobin
10.0 g/dL
Bilirubin, total
3.4 mg/dL
WBC
15,000/mm3
PT
2.7 seconds
INR
2.0
In addition to intravenous fluids, which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
An 81-year-old man with moderate dementia, Alzheimer type, is admitted to the hospital after he fell in the nursing care facility where he resides. Medical history also is remarkable for hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and stroke 5 years ago, resulting in left hemiplegia. Medications are donepezil, lisinopril, metformin, atorvastatin, and aspirin. The most recent laboratory studies in the electronic medical record were performed 2 years ago; they showed a serum urea nitrogen concentration of 38 mg/dL and serum creatinine concentration of 2.8 mg/dL. Physical examination today shows left-sided spasticity. Muscle strength is 3/5 in the left extremities. There are contractures of the left hand. On mental status examination, he is oriented to person but not to place or time. He recalls one of three objects after 5 minutes. He describes his mood as “annoyed”; affect is appropriate. He does not have suicidal ideation. Today, serum studies show a potassium concentration of 6.4 mEq/L, urea nitrogen concentration of 79 mg/dL, and creatinine concentration of 4.1 mg/dL. Although the patient has rejected hemodialysis in the past, the physician discusses the possibility of the patient’s needing long-term hemodialysis. The patient yells, “No way!” and goes on a tirade about how “doctors just want to get my money.” He is able to clearly explain his understanding that refusing treatment may result in death. Which of the following most strongly suggests that this patient has sufficient capacity to refuse hemodialysis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
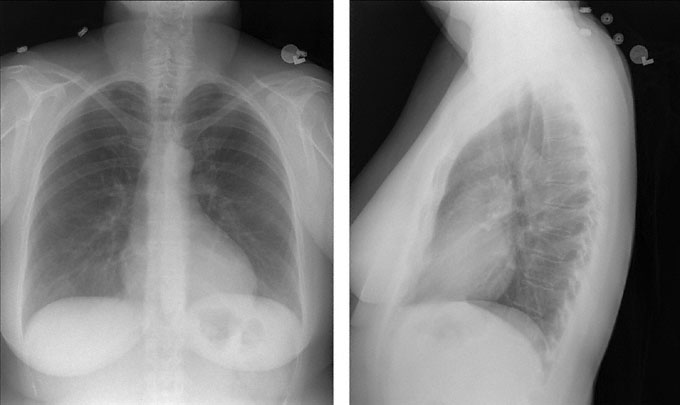
A 30-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 6-month history of intermittent wheezing. She says she was diagnosed with asthma 6 months ago and was given an albuterol inhaler to use as needed. She uses the inhaler about six times a week to control her wheezing. She says it takes approximately 10 minutes for the wheezing to disappear after using the inhaler. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable and she takes no other medications. The patient does not smoke cigarettes, drink alcoholic beverages, or use illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. Auscultation of the lungs discloses scattered expiratory wheezes at both lung bases. Peak expiratory flow rate is 350 L/min. X-rays of the chest are shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in pharmacotherapy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
A 40-year-old man has been in the hospital for the past 5 days for treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii (formerly P. carinii) pneumonia; his condition initially was improving, but he now has blurry vision in his left eye. Vision in the right eye is normal. Since admission the patient has been receiving therapy with oxygen by nasal cannula, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and prednisone. His hospital course has been uncomplicated. Medical history is remarkable for HIV infection. Vital signs today are temperature 38.0°C (100.4°F), pulse 80/min, respirations 20/min, and blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg. The patient appears chronically ill but not toxic. Auscultation of the chest discloses decreased inspiration and bilateral basilar crackles. Funduscopic examination shows exudates with hemorrhage in the left eye and a question of early exudates in the nasal quadrant of the right eye. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 10/mm3. An ophthalmologist is consulted. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
A 20-year-old white college student is brought to the office by her mother during her semester break because of an 11-kg (24-lb) weight loss during the past 4 months. The patient is a long-distance runner for the university track team. She says she does not induce herself to vomit or use laxatives, but she admits to occasionally using a sodium biphosphate enema to “clear out her system.” She also admits to occasional binge eating when she is extremely hungry or depressed. The patient says she typically runs for 1 to 2 hours prior to attending class and for approximately 1 to 2 hours during practice daily. She says, “I need to lose weight to become a champion.” The patient has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease treated with ranitidine. Her last menstrual period occurred 3 months ago. A urine pregnancy test is negative. She is 178 cm (5 ft 10 in) tall and weighs 48 kg (105 lb); BMI is 14 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 36.1°C (97.0°F), pulse 60/min, respirations 22/min, and blood pressure 94/50 mm Hg. The patient is not in distress. She appears thin. Physical examination otherwise discloses no abnormalities. ECG shows no abnormalities, and results of a serum chemistry profile, serum thyroid function tests, and complete blood count are within the reference ranges. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
A 76-year-old man is admitted to the hospital 2 hours after outpatient cystoscopy and biopsy for presumed bladder carcinoma. The procedure was complicated by brisk bleeding from the biopsy site that slowed following cauterization. A Foley catheter was inserted on admission and therapy with intravenous fluids was begun. He has been living independently at home but has had a 9-kg (20-lb) weight loss since his wife died 4 months ago; he says he has had no changes in appetite. Medical history is remarkable for hypertension controlled with lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide. He has smoked 10 cigars weekly for the past 50 years and drinks 2 alcoholic beverages weekly. He spent 46 years as a metal worker before retiring 10 years ago. He is 173 cm (5 ft 8 in) tall and weighs 59 kg (130 lb); BMI is 20 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 38.2°C (100.8°F), pulse 98/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 110/62 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 98%. There is 2+ pitting edema to the mid thighs bilaterally that is greater in the left lower extremity. Mental status examination shows no abnormalities. One hour later, the patient develops gross hematuria. He is alert and talkative and reports no discomfort. Vital signs now are temperature 38.0°C (100.4°F), pulse 102/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 102/66 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 96%. Which of the following is the most appropriate management at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
A 51-year-old woman comes to the office for an annual health maintenance examination. The patient says she has been having hot flushes lately, and her last menstrual period was 3 months ago. She says she is concerned about her risk for osteoporosis and wonders whether she should begin taking a bisphosphonate medication, which she saw advertised on television. Vital signs are normal and physical examination shows no abnormalities. DEXA scan shows a low bone mineral density. A study examining the effectiveness of the bisphosphonate medication referenced by the patient has recently been completed. The study utilized 3000 patients with osteoporosis who were randomized into placebo and bisphosphonate groups and followed for 3 years. Of the 1500 patients in the placebo group, 60 developed fractures. Of the 1500 patients in the bisphosphonate group, 30 developed fractures. Based on this information, how many patients would need to be treated with the bisphosphonate medication in order to prevent one fracture?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
A 48-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 6-hour history of left-sided facial swelling. Her symptoms initially began 5 days ago when her lips began to swell, which she thought may have been caused by an insect bite. She has not had pain, itching, or shortness of breath. She was evaluated 2 weeks ago for a 6-month history of moderate fatigue. Echocardiogram obtained at that time disclosed a dilated cardiomyopathy with an ejection fraction of 0.40. She refused cardiac catheterization. Therapy with lisinopril, metoprolol, furosemide, and potassium was initiated and today she reports that her fatigue has improved. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable and she has no known allergies. BMI is 20 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 82/min, respirations 13/min, and blood pressure 122/73 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 97%. Physical examination discloses moderate swelling of the left side of the lips and jaw; there is no warmth or erythema. Oropharynx is clear and the patient’s voice is normal. The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Diphenhydramine is administered. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
A 42-year-old man comes to the office because of a 2-month history of progressive light-headedness when rising from a seated position. Sitting for 1 to 2 minutes results in improvement. Medical history is unremarkable. He takes no prescription drugs but occasionally takes over-the-counter acetaminophen for headache and calcium carbonate for heartburn. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Vital signs while seated are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 72/min and regular, respirations 14/min, and blood pressure 108/64 mm Hg. After standing for 5 minutes, he develops mild light-headedness, and vital signs are pulse 80/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 90/52 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no other abnormalities. A complete blood count and serum electrolyte, urea nitrogen, creatinine, and calcium concentrations are all within the reference ranges. Serum catecholamine concentration is within the reference range while the patient is seated, and it does not increase significantly after the patient stands for 5 minutes. A drug with which of the following mechanisms of action is most appropriate for this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
A 56-year-old homeless woman is admitted to the hospital because of abnormal results of liver function tests obtained in the emergency department 6 hours ago for evaluation of a 6-week history of fatigue, pruritus, and dry eyes. In the emergency department, the patient also reported that her skin has appeared darker than normal and she stated that the itching has been worse at night. She has not had fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting. Medical history is remarkable for bipolar disorder. The patient currently takes no medications. She lives on the streets and occasionally sleeps in a homeless shelter. She does not drink alcoholic beverages or use illicit drugs. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 78/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 137/68 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 97%. The patient is disheveled and appears older than her stated age. Physical examination discloses dry, hyperpigmented skin and excoriations on the upper and lower extremities. Abdominal examination discloses hepatomegaly; the spleen tip cannot be palpated. There is no edema of the lower extremities. Results of initial serum laboratory studies are shown:
ALT
118 U/L
AST
130 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase
1900 U/L
Amylase
30 U/L
Bilirubin, total
2.0 mg/dL
Direct
1.3 mg/dL
Which of the following studies is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
An 85-year-old man with progressively worsening dementia, Alzheimer type, is brought to the office by his wife, because she is having difficulty caring for him at home. He is a longtime patient of the practice. He was once a busy real estate agent but now sleeps most of the day and has severe memory deficits. His wife helps him pick out his clothes in the morning, but the patient is able to shower and dress himself. He does not have significant physical difficulties. At the earlier stages of his disease, he enjoyed playing games, such as bingo. Medical history also is remarkable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Medications are hydrochlorothiazide, donepezil, memantine, and 81-mg aspirin. Vital signs are normal. The patient does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcoholic beverages. He is alert and oriented to person, place, and time but is unable to compete serial sevens or other simple calculations. He can name the current president but no prior presidents. The patient’s wife says she still wants him to live at home with her but occasionally feels that she needs a break. They have no other family in the area. The patient’s wife agrees that enrolling the patient in an adult day-care program would be helpful for both her and her husband. Which of the following is the most appropriate way to propose to the patient that he attend adult day care?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 2 items.
A 36-year-old female homemaker and part-time bookkeeper comes to the office for a refill of her fluoxetine prescription for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). She is accompanied by her 14-year-old daughter. The mother was diagnosed with OCD 4 years ago because of obsessive hand-washing and a fear of germs. Her symptoms are well controlled on this medication and she has no side effects. Today, she expresses concern for her daughter. She tells you, “She is just like I was—a worrier who has to be perfect.” The daughter is 155 cm (5 ft 1 in) tall and weighs 44 kg (98 lb). The girl is anxious but has no known obsessions. She does have a nervous facial tic that has been present intermittently for several months. The mother asks, “Is my condition hereditary?”
Item 1 of 2
Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
Item 2 of 2
Which of the following factors is most concerning about the daughter’s risk for OCD?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
A 55-year-old woman is examined in the hospital 12 hours after undergoing resection of non-small cell lung carcinoma in the right upper lung lobe. She has a history of right shoulder pain, hypertension, deep venous thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Current medications are enoxaparin, hydrochlorothiazide, and oxycodone. A retrievable inferior vena cava filter was placed prior to the operation. BMI is 20 kg/m2. Temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), pulse is 86/min, respirations are 24/min, and blood pressure is 132/64 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on 2 L of oxygen via nasal cannula shows an oxygen saturation of 94%. Physical examination shows drooping of the right eyelid, unequal pupil sizes (with the right being smaller than the left), facial flushing, and right upper extremity pain and weakness. The most likely cause of these findings in this patient occurred as a result of resection of which of the following structures?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
A 79-year-old man is brought to the office by his daughter because of a 1-week history of thoughts that she is trying to “trick me and steal from me.” During the past 3 years, the patient has had progressive forgetfulness, including difficulty recalling events from earlier in the day, names of family members, and recent major news events. His childhood memories are intact. During the past year, he has been getting lost while walking or driving in his neighborhood. He now can no longer drive his car and relies on others to drive him. Six months ago, the daughter hired a caregiver to assist her father in activities of daily living. The patient has no history of psychiatric illness and takes no medications. His father had a cerebral infarction at the age of 60 years. The patient is alert but appears mildly disheveled. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse is 80/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. Neurologic examination shows normal movement of all extremities and a normal gait. On mental status examination, he has a restricted affect and mildly anxious mood. He is fully oriented. He recalls zero of three objects after 5 minutes and is unable to perform serial sevens. He has not had suicidal or homicidal ideation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
A 62-year-old white woman comes to the clinic because of a 5-day history of dysuria and urinary frequency. She has had recurrence of similar symptoms since undergoing hysterectomy 2 years ago. Last month, she was evaluated for similar symptoms and treated for a urinary tract infection. She has no other history of serious illness and takes no medications. Examination shows no abdominal or costovertebral angle tenderness. Urinalysis shows a specific gravity of 1.010 (N=1.003–1.029) and is negative for glucose, protein, nitrites, and leukocyte esterase. Which of the following is the most likely finding on pelvic examination in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
A 36-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 6-month history of episodes of discomfort in her legs that causes her to feel like she has to move her legs around for relief. The patient says the discomfort is worse when she is tired and often makes it hard for her to fall asleep. Medical history is significant for a peptic ulcer. She currently takes no medications. Family history is unremarkable. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 36.7°C (98.1°F), pulse 82/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 134/86 mm Hg. Neurologic examination discloses no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic study to obtain at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
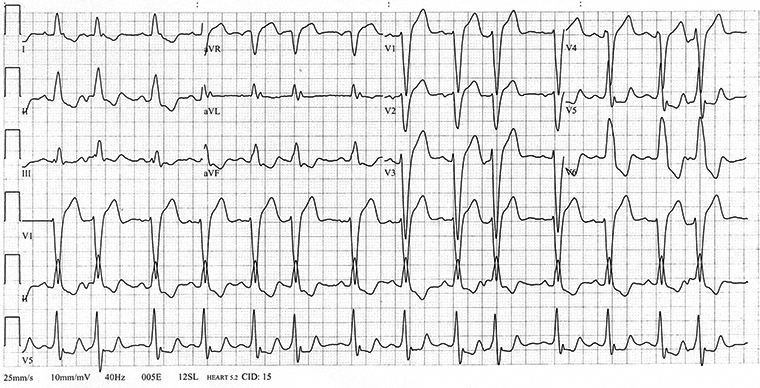
A 76-year-old man comes to the office because of a 1-month history of shortness of breath, especially while gardening. He has had shortness of breath on exertion in the past, but not as severe as this. He also reports having a sharp pain in the left side of his chest after removing large stones from the garden; the pain “eased off” after several hours and has not recurred. He is on a low-cholesterol, low-salt diet for mild hypercholesterolemia and borderline hypertension. Medical history also is remarkable for arthritis and mild emphysema. Medications are atorvastatin and ibuprofen. The patient is a retired vice president of a utilities corporation. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 55 years. Vital signs are pulse 78/min and regular and blood pressure 165/95 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination discloses decreased breath sounds throughout and a new grade 2/6 holosystolic murmur heard best in the fourth intercostal space at the anterior axillary line, but no other abnormalities. There is no edema of the lower extremities. ECG is shown. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the ECG finding in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
A 59-year-old man comes to the office because of a 2-month history of worsening shortness of breath that has made it difficult to continue working at his job as a miner, which has been his occupation for the past 30 years. The patient reports no recent illnesses and has not had chest pain, discomfort, or weight loss. Medical history is unremarkable and he takes no medications. He has no known allergies. He does not smoke cigarettes. There are no pets in his home. Vital signs are within normal limits. Auscultation of the lungs discloses diminished breath sounds in all lung fields. The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial diagnostic study?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the office for his first visit as a new patient. He says he has felt well but admits to having a poor memory when it comes to providing medical history, which is remarkable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia, currently treated with amlodipine and atorvastatin, respectively. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 45 years and drinks three alcoholic beverages weekly. He notes exertional dyspnea and occasional cramps in his legs when he walks. He has not had abdominal pain, change in bowel habits, or urinary symptoms. He is 178 cm (5 ft 10 in) tall and weighs 68 kg (150 lb); BMI is 22 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 80/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 110/95 mm Hg. There is no jugular venous distention, but the intensity of the carotid upstroke is diminished. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination discloses a grade 3/6 harsh, crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur that radiates to the carotid arteries. There is an audible S4 but no S3 gallop. Abdominal examination discloses no abnormalities. Pedal pulses are mildly diminished. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. Results of laboratory studies are shown:
Serum
Blood
Cholesterol
Hemoglobin
12.0 g/dL
Total
180 mg/dL
HDL
40 mg/dL
LDL
110 mg/dL
Triglycerides
150 mg/dL
Urea nitrogen
15 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.2 mg/dL
ECG shows regular sinus rhythm and left ventricular hypertrophy. At this time, it is most appropriate to inquire about which of the following potential symptoms to help explain the pertinent examination findings?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
A female newborn is examined in the hospital nursery shortly after birth to a gravida 2, para 2 woman. The mother’s prenatal course was complicated by preeclampsia that was successfully treated with methyldopa. The patient was born via cesarean delivery because of failure of labor to progress. Apgar scores were 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. The newborn is 48 cm (19 in; 25th percentile) long and weighs 3200 g (7 lb; 25th percentile); head circumference is 35 cm (14 in; 50th percentile). Vital signs are temperature 36.7°C (98.1°F), pulse 144/min, and respirations 48/min. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 94%. Physical examination discloses a dark-brown, hyperpigmented, well-circumscribed lesion on the left buttock measuring 8 cm in diameter. This patient is most likely to develop which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
A 65-year-old woman comes to the office for a routine health maintenance examination. Menopause occurred 12 years ago. Medical history is significant for hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine. Family history is unremarkable. The patient does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcoholic beverages. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Screening DEXA scan is ordered, and results show a femoral neck T-score of −1.4. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy to recommend for this patient’s bone health at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
A 33-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 2-month history of heavy bleeding with menses. Her menstrual periods now typically occur every 32 days and last for 7 days; each period requires use of approximately 8 to 10 sanitary pads daily. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable and she takes no medications. She drinks two to four alcoholic beverages on weekends and does not smoke cigarettes. She is not currently sexually active and has no history of sexually transmitted infection. Pap smear obtained 2 years ago showed no abnormalities. Her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. BMI is 23 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination discloses no conjunctival pallor. There are buccal petechiae as well as a few scattered ecchymoses on all extremities. The remainder of the examination, including bimanual pelvic examination, discloses no abnormalities. Pap smear is obtained and results are pending. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Results of laboratory studies are shown:
Blood
Hematocrit
38.2%
Hemoglobin
11.6 g/dL
WBC
7400/mm3 with normal differential
Platelet count
26,000/mm3
Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
A 30-year-old female schoolteacher, with a 1-year history of intermittent episodes of urinary urgency and frequency, returns to the office because the symptoms have increased in frequency during the past 6 months. During the episodes, her voiding generally produces only a small volume of urine. She has difficulty sleeping through the night because of urinary urgency and frequency. She also has had intermittent pelvic pain. Her symptoms have been treated with antibiotic therapy in the past, but she never has had a positive urine culture. Medical history otherwise is unremarkable. She had been sexually active with one male partner prior to onset of her symptoms. She used condoms for contraception. BMI is 25 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 36.1°C (97.0°F), pulse 80/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 130/75 mm Hg. Physical examination discloses no costovertebral angle tenderness. Pelvic examination discloses mild tenderness to palpation of the bladder and anterior vaginal wall. Results of complete blood count are within the reference ranges. Results of urinalysis are shown:
Color
Yellow
Specific gravity
1.022 (N=1.003–1.029)
Protein
Negative
Glucose
Negative
WBCs
2–3/hpf
RBCs
None
Squamous epithelial cells
5–10/hpf
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect