Step 3 – NBME 7 – Block 3
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
A 57-year-old woman with advanced emphysema is admitted to the hospital because of hypoxemia from pneumococcal pneumonia in the right middle and lower lung lobes. Routine medications are albuterol, ipratropium, prednisone, and moxifloxacin. After 5 days of antibiotic therapy, the patient continues to require 2 L/min of supplemental oxygen to maintain oxygen saturation levels greater than 89%. Leukocyte count is now normal, and chest x-ray shows partial resolution of infiltrates. Which of the following is the most accurate statement regarding this patient’s course?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
A 59-year-old white man comes to the office for evaluation of a 3-week history of substernal chest pain with exertion that occasionally radiates to the left anterior chest. The pain lasts approximately 30 seconds, resolves with rest, and is accompanied by sweating and mild nausea, which also remits with rest. Medical history is significant for mild hypercholesterolemia. The patient smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years; he stopped smoking approximately 5 years ago. He is currently without pain. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 90/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 150/90 mm Hg. Physical examination discloses a left carotid bruit and no other abnormalities. ECG shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate additional study to order at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
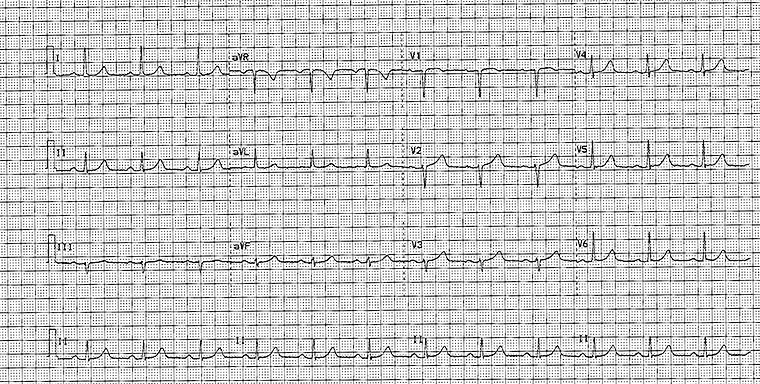
A 14-year-old boy of Japanese descent is brought to the clinic because of a 2-month history of progressive fatigue and weakness while playing soccer. He says that he often develops leg pain and cramping while at practice. He has noted that after performing 30 sit-ups, his abdominal muscles become stiff and he cannot continue; however, if he briefly rests, he can perform the same number of sit-ups again. Medical history is unremarkable. Vital signs are pulse 75/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 111/63 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows hepatomegaly. His creatine kinase activity is 359 U/L (N=25−90). ECG is shown. Chest x-ray shows no abnormalities. The most likely cause of the findings in this patient is a mutation in which of the following genes?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
A 9-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents because of an 8-hour history of progressive, non-itchy swelling of her face, hands, arms, and legs. The parents gave the patient an over-the-counter antihistamine 4 hours ago, but this had no effect on her symptom. The parents say that the patient’s skin appeared red prior to the swelling. The patient says she felt “tingly.” She has had mild nausea but no fever. She has no history of atopic dermatitis, allergen exposures, or asthma. There has been no change in her diet, exercise, or bathing regimens. She appears to be in mild distress. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 110/min, respirations 15/min, and blood pressure 100/65 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 97%. Physical examination shows 1+ to 2+ nonpitting edema of the face (including perioral and periorbital areas) and all extremities without erythema, fluctuance, or vesicobullous formation. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Results of a complete blood count and serum electrolyte concentrations are within the reference ranges. Serum C4 concentration is decreased; serum C1q and C3 concentrations are within the reference ranges. The most likely cause of the clinical findings in this patient is an abnormality in which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
A 22-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis is brought to the clinic because of a 2-week history of a flare of symptoms. During this time, she has been unable to work or go to school. During the past week, she has had severe fatigue and has been unable to perform her activities of daily living despite her current medication regimen. She says, “The most difficult part of all of this is not being able to play with and take care of my 3-year-old daughter. She is so active and wants to play all the time, and I’m not even able to get out of bed.” Which of the following is the most appropriate physician response?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
An 18-month-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because of an 8-hour history of fever and urinary incontinence. Medical history is unremarkable. The patient is at the 19th percentile for length and the 45th percentile for weight. Vital signs are temperature 38.0°C (100.4°F), pulse 102/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 96/72 mm Hg. The child appears mildly irritable. Physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Results of urinalysis are shown:
pH
6.0 (N=4.5–7.8)
Protein
Trace
Blood
Small
Leukocyte esterase
Positive
Nitrite
Positive
RBCs
5–8/hpf
WBCs
20–30/hpf
Bacteria
Positive
In addition to starting a 7-day course of cefixime and obtaining urine cultures, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
A 56-year-old woman is being prepared for discharge from the emergency department following management of a complete rupture of her left Achilles tendon. The patient’s medical insurance consists of a preferred provider organization plan, and she is referred to an orthopaedic surgeon who is in her insurance plan’s provider network for repair of her injury. However, the patient requests referral to a different surgeon at a specialty hospital instead because the surgeon has a reputation for being the best in repair of her type of injury. Which of the following is the most likely cost-related implication for this patient regarding her decision to seek treatment from the out-of-network surgeon?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
A 25-year-old woman with alcohol use disorder comes to the Veterans Affairs clinic for a follow-up examination 2 weeks after being treated in the hospital for alcohol intoxication and alcohol-induced seizures. She was discharged from the US Army 3 years ago. During the patient’s hospital stay, she was treated with diazepam, and naltrexone therapy was initiated prior to discharge. Now, she tells the physician that she stopped taking naltrexone when she left the hospital because she wanted to understand all the treatment options for alcohol use disorder before continuing with the naltrexone therapy. She adds that she is hoping to become pregnant soon. She successfully completed an alcohol rehabilitation program years ago but relapsed 1 year ago. She is motivated and says she realizes all the damage alcohol has done in her life and she wants treatment that will make her quit “for good.” She wants a medication that will decrease her desire to drink and her cravings for alcohol. She has no other history of major medical illness and takes no other medications. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Renal and liver function studies disclose no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
A 42-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, is admitted to the hospital to undergo myomectomy for leiomyomata uteri. She is currently receiving treatment because of a 4-year history of secondary infertility. She has two children from a previous marriage and is trying to conceive with her current husband. Her first pregnancy at the age of 22 years resulted in a spontaneous vaginal delivery, and her second pregnancy resulted in a cesarean delivery because of failure to progress during labor. Menses had occurred at regular 27-day intervals until 2 years ago, when her menstrual bleeding became heavier and longer, extending up to 7 days. She also has had severe pain with sexual intercourse, especially on deep penetration. She had an appendectomy at the age of 16 years. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and she currently takes no medications. BMI is 25 kg/m2. Vital signs, including oxygen saturation, are within normal limits. Physical examination shows an enlarged uterus consistent with a 17-week gestation that is confirmed on pelvic ultrasonography, which also showed numerous subserosal nodules. Hysterosalpingography and laparoscopy disclose left tubal occlusion, multiple small red and brown lesions over the pelvic sidewalls, uterosacral ligaments, and fallopian tubes, as well as adhesions between the anterior uterine serosa and anterior abdominal wall. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient’s dyspareunia?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
A 57-year-old woman with end-stage kidney disease is evaluated in the hospital 3 days after admission for a 1-day history of fever. One month ago, she began hemodialysis through a left internal jugular venous catheter while awaiting maturation of an arteriovenous fistula that had been surgically placed in her right upper extremity 8 weeks earlier. Blood cultures obtained on admission and on hospital day 2 grew oxacillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, prompting removal of the patient’s catheter yesterday. Intravenous oxacillin therapy was initiated and hemodialysis was restarted using her arteriovenous fistula. Medical history also is remarkable for type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Routine medications are insulin, lisinopril, and daily aspirin. Temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F), pulse is 78/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 144/86 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 96%. The catheter removal site appears to be healing well; there is no erythema, drainage, or warmth. Examination of the fistula in the right upper extremity discloses a palpable thrill. Cardiac examination discloses a grade 2/6 systolic murmur that is unchanged from 6 months ago. A culture of the tip of the removed catheter shows growth of oxacillin-sensitive S. aureus. Results of repeat blood cultures obtained today are pending. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
A 32-year-old woman comes to the office because of a 2-month history of difficulty sleeping resulting in fatigue. She says she has been having trouble getting along with her family because of her irritable mood. She sometimes takes alprazolam, which she obtained from a friend. She is a nurse, and her schedule changed a few months ago so that she works 11:00 pm to 7:00 am four nights weekly. She sometimes sleeps before work and sometimes after work. She has lost 2.3 kg (5 lb) during the past 2 months. She is 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) tall and weighs 61 kg (135 lb); BMI is 21 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.2°C (99.0°F), pulse 82/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 128/74 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
A 13-year-old white girl is admitted to the hospital for emergency dilatation and curettage for an incomplete spontaneous abortion. She is unsure of the date of her last menstrual period. She has intellectual developmental disorder and attends a special school program within a rural school system. She is reported to have an IQ of 70 with fairly good verbal skills. She lives at home with her mother, who has a history of alcohol use disorder, and her biological father is unknown. The mother did not know that her daughter was pregnant. The patient has been diagnosed with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder and her mother says that the girl often displays mood swings and intrusiveness. She does not take any medications. Her mother suspects that the patient has been sexually active since menarche at age 12 years with two teenaged boys in their neighborhood, as well as with the mother’s male companion. The patient is 157 cm (5 ft 2 in) tall and weighs 59 kg (130 lb). Physical examination is consistent with fetal alcohol syndrome. Regarding the patient’s sexual history and pregnancy, which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
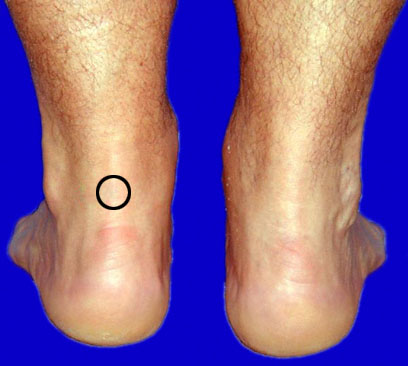
A 49-year-old man comes to the office because of left ankle pain that he first noticed on awakening this morning. Bearing weight on the foot caused intense pain. As the day progressed, the pain decreased but did not resolve completely. He has not had similar pain in the past. Medical history is unremarkable and he takes no medications. He exercises at a fitness facility regularly and states that he has been preparing to run a marathon. He is 180 cm (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 100 kg (220 lb); BMI is 31 kg/m2. When asked to indicate the point of maximum pain, he indicates the area outlined in the photograph. The foot is neurovascularly intact; however, passive dorsiflexion of the foot increases the pain. The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
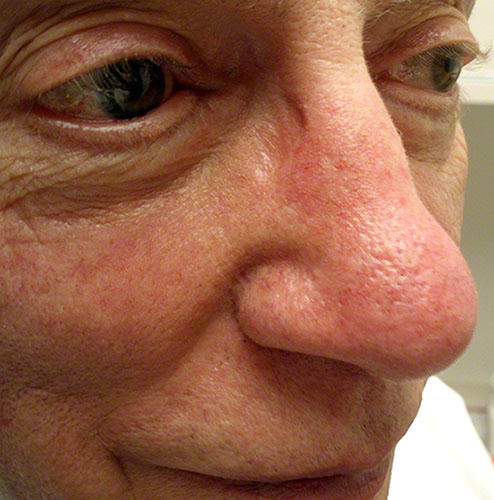
A 58-year-old man comes to the office because of a 9-month history of increased redness of his face that occurs mainly on his nose and cheeks. He also has had intermittent raised papules on his face. His symptoms worsen during the summer. He has not had joint pain, fatigue, or rash in any other location. He has changed his brand of shaving cream twice, but the rash has persisted. Medical history is remarkable for seasonal allergies treated with loratadine. Family history is remarkable for systemic lupus erythematosus in a sister. He drinks three to four alcoholic beverages daily and has smoked a pipe for 10 years. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination discloses the findings shown in the photograph. The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Which of the following most likely contributes to this patient’s condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
An 80-year-old woman is brought to the office by her son because of a 3-month history of progressive withdrawal from social and family interactions. Her last examination was 1 year ago; the patient’s son says he could not convince her to agree to come in to the office before now. He has been assisting his mother with shopping and meal preparation during the past 6 months. Medical history is remarkable for hypertension that had been treated with hydrochlorothiazide; the patient stopped taking her medication 2 months ago. She has had a 9-kg (20-lb) weight loss during the past 12 months. Today, BMI is 17 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 85/min and irregularly irregular, respirations 12/min, and blood pressure 150/75 mm Hg. The patient appears tired and listless, and she interacts poorly with the physician and her son. Examination of the neck discloses a multinodular goiter. The remainder of the examination discloses no abnormalities. Results of laboratory studies are shown:
Serum
TSH
<1 μU/mL
Triiodothyronine (T3) resin uptake
45%
Free T4
2.0 ng/dL (N=0.7–1.8)
Which of the following is the most appropriate next diagnostic study?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 2 items.
You attend the birth of a male neonate who is born at 36 weeks’ gestation. The newborn’s birth weight is 2100 g (4 lb 10 oz), length is 44 cm (17 in), and head circumference is 31 cm (12 in). The mother has been taking methadone daily as treatment for her substance use disorder. She also admits to occasional intravenous heroin and cocaine use during this pregnancy.
Item 1 of 2
Which of the following is the most accurate statement concerning this neonate?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
Item 2 of 2
If this newborn is experiencing opioid withdrawal, you would also expect him to have which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
A 44-year-old white schoolteacher who has been your patient for the past 5 years returns to the office to request a prescription for sildenafil. He says he gets erections that are firm, but for the past several months he has been unable to achieve orgasm. He is happily married, and he and his wife have been having sexual relations about twice per week, usually on weekends. He has had no extramarital relationships. Medical history is remarkable for seasonal affective disorder, for which he takes fluoxetine. Previous periodic health evaluations and routine screening laboratory studies have been normal. Today blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg. Pedal pulses are good. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Blood glucose concentration is 105 mg/dL and urinalysis is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
A 9-year-old Hispanic boy with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is brought to the office by his mother for a follow-up visit. Since he began treatment with methylphenidate 6 months ago his behavior has improved at school. His last report card showed grades of A’s and B’s with satisfactory conduct. His mother reports there are no problems with sleep or appetite, but that he is irritable and overactive on the weekends. She says that his misbehavior outside of school continues to be a problem despite initiation of a behavioral program that you recommended to them when you prescribed methylphenidate therapy. She is also worried because he does not play with any other children. He currently takes methylphenidate in the morning and at noon only on school days. He is 142 cm (4 ft 6 in; 95th percentile) tall and weighs 34 kg (75 lb; 70th percentile). Vital signs now are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 98/min, respirations 15/min, and blood pressure 90/60 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
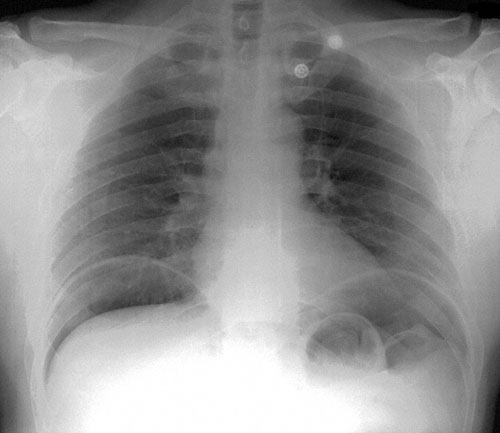
A 43-year-old woman, who was admitted to the hospital 8 hours ago because of a 1-day history of intractable nausea and vomiting, now is reporting shortness of breath and severe retrosternal chest pain. She rates the pain as a 10 on a 10-point scale. Emesis has persisted since admission, despite promethazine therapy. Medical history is significant for alcohol use disorder during the past 10 years and hypertension. Her only routine medication is metoprolol. She has no allergies. She does not smoke cigarettes or use illicit drugs. She drinks four to six beers daily. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse 115/min, respirations 27/min, and blood pressure 98/65 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on oxygen at 4 L/min via nasal cannula shows an oxygen saturation of 93%. The patient is breathing rapidly and appears to be in mild respiratory distress. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination discloses crepitus on palpation of the chest. Abdomen is diffusely tender on palpation. The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Chest x-ray is shown. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
A 2-month-old girl is brought to the clinic by her parents because of a 2-week history of fussiness. The parents report that their daughter cries easily and is sometimes inconsolable, especially when they put her in the crib. She is exclusively breast-fed and has no difficulty with eating. Medical history is unremarkable and she receives no medications. She is 57 cm (22.5 in; 50th percentile) long and weighs 4990 g (11 lb; 50th percentile). Vital signs are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
A 43-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital for treatment of a 10-day history of worsening diarrhea, dehydration, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, and generalized weakness. Treatment with over-the-counter antidiarrheal medications has not improved her symptoms. This is her third hospital admission within the past 18 months for similar symptoms. Examination on both previous admissions showed no abnormalities. She says that she was admitted to another hospital 6 weeks ago for similar symptoms. The patient refuses to sign a release for records of this hospitalization, because “the care there was so lousy, the records wouldn’t tell you anything.” Medical history otherwise is unremarkable. She has had no changes to her diet and takes no other medications. She has worked as a nursing assistant but is currently unemployed. Pulse is 102/min and blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg. She appears to be in mild distress and cachectic. On mental status examination, she is watchful and appears suspicious of hospital staff. She has a mildly depressed mood and constricted affect. She is attentive when inquiring about the test results. Serum creatinine concentration is 1.3 mg/dL; results of other laboratory studies are within the reference ranges. Urinalysis shows no abnormalities. The patient states, “I hope you’ll do a better job of figuring this out than the other hospital.” Which of the following is the most appropriate physician response?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
A 21-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after he was rescued from a fire 45 minutes ago at the auto repair shop where he works. He was found on the floor unconscious and surrounded by flames. At the scene, paramedics started high-flow oxygen via face mask as well as intravenous fluids. On arrival, the patient is alert and fully oriented. Temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 95/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on 100% oxygen via nonrebreather mask shows an oxygen saturation of 95%. Physical examination discloses singed facial hair and charcoal smudges over the face. There are second-degree burns to the nose and ears, and first-degree burns to the neck, hands, and feet. Examination of the pharynx reveals blistering and minimal edema. Auscultation of the lungs discloses bilateral rhonchi. Which of the following findings is most critical in determining this patient’s need for endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 6-hour history of sharp chest pain. He says the pain is located in the center of his chest, does not radiate, and is unaffected by inspiration, exertion, or change of position. He does not recall any trauma or heavy lifting. He has not had any associated nausea, dizziness, or difficulty breathing. Medical history is remarkable for hyperlipidemia and hypertension. His current medications are lisinopril, atorvastatin, and 81-mg aspirin. He has smoked one-half pack of cigarettes daily for the past 20 years. Temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse is 72/min, respirations are 12/min, and blood pressure is 135/80 mm Hg. Cardiopulmonary examination discloses no abnormalities. Serum LDL-cholesterol concentration is 85 mg/dL. Results of ECG show T-wave inversions in the lateral leads. A case-control study of 500 men presenting to the emergency department with chest pain shows that the findings on this patient’s ECG were also present in 50% of men with acute myocardial infarction and in 10% of men who did not have acute myocardial infarction. Which of the following describes the extent to which obtaining these ECG findings alters the statistical probability that this patient has acute myocardial infarction?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
A 2-month-old female infant is brought to the office by her mother for disclosure of genetic testing results. The patient was born at term via spontaneous vaginal delivery. At birth, she was noted to have dysmorphic features, a small ventriculoseptal defect, and a single kidney. She began having seizures 48 hours after delivery; MRI of the head disclosed polymicrogyria. Phenobarbital therapy was initiated. Postnatal karyotype disclosed an unbalanced chromosomal translocation. The patient’s mother also has undergone genetic testing, which disclosed a balanced translocation. The patient’s maternal aunt, who has had four miscarriages, is currently at 18 weeks’ gestation. The physician suspects that the maternal aunt could also be a carrier of a balanced translocation and recommends that the patient’s mother share this information with her as it could have implications for the ongoing pregnancy. The patient’s mother says that she does not want anyone to know about this chromosomal abnormality. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
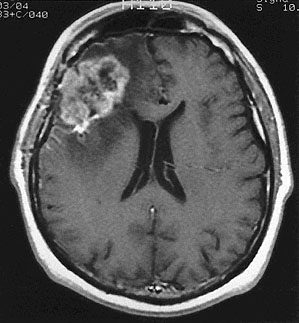
A 55-year-old man is brought to the emergency department via ambulance 20 minutes after he was found unconscious next to his car in a parking lot. It is estimated that he was unconscious for approximately 30 minutes before he was found. On arrival, he is awake. His wife reports that he has been acting “differently” during the past 2 weeks; she says he asked her how to write out a check and was unable to remember the names of several close friends. Medical history is unremarkable. His only medication is a daily multivitamin. He is active and runs 3 miles daily. He does not smoke cigarettes. He drinks one to two alcoholic beverages weekly. BMI is 22 kg/m2. Temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 130/82 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 97%. The patient is oriented to person but not to place or time. Neurologic examination shows no other focal findings. MRI of the brain is shown. In addition to highly atypical cells, histologic examination of a biopsy specimen of the lesion is most likely to show which of the following findings in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
A 17-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her mother 30 minutes after she attempted to stab herself in the abdomen “to get the evil spirits out.” She had been well until yesterday, when she began to be increasingly withdrawn and anxious. Her father died unexpectedly 1 week ago and his funeral was yesterday. The patient is described by her family as always being “prone to overreacting,” but she never has had any previous mental health evaluations or treatment. Medical history otherwise is remarkable for mild asthma treated with inhaled albuterol as needed. BMI is 24 kg/m2. Temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 17/min, and blood pressure is 122/72 mm Hg. The patient appears alert but is unresponsive to most questions, making such statements as, “I’m next if I don’t get them out of me.” The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
The following vignette applies to the next 2 items.
A 45-year-old white woman comes to the office to discuss results of studies that were obtained 1 week ago to evaluate fatigue. She has been experiencing fatigue for the past 10 months. At her last visit, physical examination disclosed no abnormalities and screening laboratory studies were within the reference ranges. Psychiatric evaluation indicated that her symptoms are likely due to major depressive disorder with seasonal pattern. She says her sister was diagnosed with the same disorder and asks if light therapy would effectively resolve her own symptoms. You review the medical literature and find four randomized controlled trials comparing bright white light therapy to a control. Results are shown:
Studies of Bright White Light Therapy
Study
Subjects
Control
Control Group
Response Rate (%)
Active Group
Response Rate (%)
P value
A
45
No light
10
80
0.025
B
75
No light
25
65
0.049
C
60
Red light
57
74
0.11
D
120
Red light
18
70
0.037
Item 1 of 2
Which of the following is the most likely reason that study C showed a nonstatistical difference in response rates?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
Item 2 of 2
Based on the results reported in these four studies, which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation to this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
A 40-year-old woman comes to the office because of progressive cough, blood-tinged sputum, and difficulty breathing on exertion during the past 14 days. She reports no chest pain. Medical history is unremarkable and she takes no medications. Vital signs are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 90/min, respirations 20/min, and blood pressure 110/80 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 93%. Examination of the neck discloses jugular venous distention with prominent a waves. Auscultation of the chest discloses an opening snap followed by a low-pitched diastolic rumble heard best with the patient in the lateral decubitus position. Which of the following is the most likely valvular heart abnormality in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
A 2-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents because of the child’s sudden refusal 1 hour ago to move her left arm. The parents are not aware of any trauma and she has never refused to move her left arm in the past. Medical history is unremarkable. This is the first time the child has been brought to the emergency department. She is tearful and is holding her left arm slightly flexed at the elbow and pronated at the forearm. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination discloses no additional abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
A 23-year-old man with type 1 diabetes mellitus is admitted to the hospital because of a 2-day history of light-headedness, headache, vomiting, and diffuse abdominal pain. He ran out of his prescribed insulin 3 days ago. Vital signs on admission are temperature 36.7°C (98.0°F), pulse 120/min, respirations 26/min, and blood pressure 104/70 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 99%. Physical examination discloses a soft abdomen with mild diffuse tenderness but no guarding or rebound. Results of serum laboratory studies are shown:
Urea nitrogen
30 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.8 mg/dL
Na+
128 mEq/L
K+
5.4 mEq/L
Cl−
92 mEq/L
HCO3−
8 mEq/L
Glucose
520 mg/dL
Ketones
1:32
Therapy with intravenous 0.9% saline and an insulin drip is initiated. Four hours later, pulse is 80/min and blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. Repeat physical examination discloses a soft abdomen without tenderness; bowel sounds are normal. Results of repeat serum laboratory studies are shown:
Urea nitrogen
20 mg/dL
Creatinine
1.4 mg/dL
Na+
136 mEq/L
K+
4 mEq/L
Cl−
103 mEq/L
HCO3−
14 mEq/L
Glucose
132 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most appropriate change in the patient’s therapy?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
A 32-year-old man comes to the office because of a 4-day history of fever to 39.4°C (103.0°F), malaise, crampy abdominal pain, diarrhea, and muscle aches. He has had six to eight episodes of small-volume diarrhea daily. During the past 2 days, he has noticed blood and mucus mixed in his stool. He has not had nausea but has not had an appetite during his illness. The patient’s wife developed a similar illness yesterday. The patient’s medical history is unremarkable and he takes no medications. He has taken bismuth with no relief of his symptoms. He has no history of recent travel. Vital signs are temperature 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse 88/min, respirations 14/min, and blood pressure 124/80 mm Hg. Physical examination discloses moist mucous membranes. Abdomen is soft with mild lower quadrant tenderness but no guarding. Rectal examination discloses a small amount of loose stool with gross blood. Examination of the stool shows fecal leukocytes. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s illness?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
A 20-year-old white man who works as a carpenter’s apprentice comes to the emergency department because of a burn of his right hand and arm. He told the emergency department physician, “I was working on a framing project for a new apartment building when I hammered a nail into a live wire. It shocked me, and my palm is burned where I was holding the hammer. Now my whole arm hurts, too.” He had no other injuries or complaints. He did not lose consciousness, nor was he knocked down by the shock. He has no medical problems and takes no medications. He reports drinking five to six bottles of beer daily, smoking marijuana almost daily, and snorting cocaine about two to three times weekly. He has no allergies. His last tetanus vaccination was 4 years ago, when he required stitches in his head after a fall. Vital signs in the emergency department are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 98/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 142/88 mm Hg. Physical examination discloses a deep second-degree burn of the right palm in the shape of the hammer handle. There is tenderness to the forearm up to the elbow. He has good radial and ulnar pulses, and capillary refill time in the fingers of the right hand is 1 second. Sensation to pinprick is normal in the right hand. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic study at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
A 44-year-old Indian woman is brought to the emergency department by her family after she collapsed at home. Her husband says that she has had a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss, low-grade fever, occasional night sweats, and increasing fatigue during the past 10 weeks. She has been taking levofloxacin for 1 week because of a presumed urinary tract infection. Her only other medication is over-the-counter iron tablets for treatment of anemia. The patient immigrated to the USA 8 years ago from India and had been generally healthy. Family history is remarkable for diabetes mellitus and iron deficiency anemia. Her mother died at age 49 years from tuberculosis. The patient does not smoke cigarettes, drink alcoholic beverages, or eat meat. She is 156 cm (5 ft 1 in) tall and weighs 42 kg (92 lb); BMI is 17 kg/m2. Vital signs now are pulse 120/min to 140/min, respirations 28/min, and blood pressure 90/46 mm Hg while supine; and 74/46 mm Hg palpable while sitting. She is in moderate distress but responds to questions. Physical examination discloses decreased skin turgor and increased pigmentation of the antecubital fossae; mucous membranes are dry. Neck is supple without lymphadenopathy, and lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination discloses an S1, a physiologically split S2, and an S4 without an S3 gallop. Abdomen is flat and bowel sounds are diminished. There is mild bilateral costovertebral angle tenderness. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. Results of laboratory studies are obtained and shown:
Serum
Blood
Urea nitrogen
44 mg/dL
Hematocrit
48.2%
Creatinine
1.2 mg/dL
Hemoglobin
15.7 g/dL
Na+
118 mEq/L
WBC
13,400/mm3
K+
6.6 mEq/L
Urine
Cl−
90 mEq/L
Glucose
Negative
HCO3−
14 mEq/L
Nitrites
Negative
Glucose
72 mg/dL
pH
5.5
Specific gravity
1.025
Arterial blood gas analysis on room air
Leukocyte esterase
1+
Po2
104 mm Hg
Protein (dipstick)
1+
Pco2
22 mm Hg
WBC
20–40/hpf
pH
7.18
RBC
3–7/hpf
Urine culture (obtained 1 week ago)
No growth in 48 hours
At this time, which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic study to evaluate the patient’s hypotension?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
A 46-year-old man is undergoing treatment in the hospital for complications from AIDS. The patient has been HIV-positive for the past 15 years and has had AIDS for the past 5 years. He is known to be addicted to heroin and cocaine. He currently has AIDS-related dementia, pneumocystis pneumonia, and cytomegalovirus esophagitis. He has required mechanical ventilation for the past 3 weeks. He is 178 cm (5 ft 10 in) tall and weighs 41 kg (90 lb); BMI is 13 kg/m2. CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is less than 50/mm3. Vital signs today are temperature 38.1°C (100.6°F), pulse 100/min, and blood pressure 100/60 mm Hg. The abdomen is distended. Mental status examination discloses marked obtundation. CT scan of the abdomen shows free air in the region of the right colon. Surgical consultation indicates that the patient is not a candidate for an operation. The patient does not have an advance directive, and the family has requested that everything possible be done. You believe that his course is terminal and should not be prolonged. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step regarding his end-of-life needs?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
An 18-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 0, aborta 1, at 39 weeks’ gestation comes to the office because of an 8-hour history of contractions. She says, “The contractions are getting stronger. For the past 3 hours, they’ve been coming every 5 minutes.” She has received prenatal care since 12 weeks’ gestation. Her membranes have not ruptured and she has not had vaginal bleeding. She says she feels the baby moving. Medical history is significant for an anxiety disorder, an induced abortion at age 16 years, and an appendectomy at age 10 years. Medications include prenatal vitamins. Vital signs are temperature 36.8°C (98.2°F), pulse 88/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 106/72 mm Hg. Fundal height is 36 cm with an audible fetal heart rate of 132/min. The cervix is 4 cm dilated and 100% effaced, and the vertex is at +1 station with intact membranes. Leopold maneuver estimates a fetal weight of 3400 g (7 lb 8 oz). In her birth plan, the patient has outlined her desire to avoid intervention as much as possible, including oxytocin augmentation, epidural analgesia, and intravenous fluids. She will have a doula present during her labor. Which of the following factors most strongly indicates a good prognosis for vaginal delivery?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
A 48-year-old Hispanic American woman returns to the office for a routine gynecologic examination. She is generally healthy and says she has felt well. One year ago, she underwent total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy for treatment of symptomatic leiomyomata uteri. She has been taking estradiol since the procedure. She takes no other medications. Results of Pap smears obtained in the past have all been normal. Vital signs are normal and physical examination shows no abnormalities. The patient asks, “Now that I’ve had a hysterectomy, how often should a Pap smear be done?” Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation to the patient for having a Pap smear?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
A 20-year-old college student is brought to the university health center by his roommate because of chest pain and shortness of breath that began suddenly 45 minutes ago while the patient was jogging. He typically jogs 3 miles 4 days weekly, but today, after jogging for 1½ miles, he noted the sudden onset of pain in his left upper chest anteriorly. He initially ignored the pain and continued jogging, but he stopped due to a lack of energy and increasing shortness of breath. En route to the health center, his breathing was less labored but his chest pain persisted. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable. He takes no medications. The patient is 188 cm (6 ft 2 in) tall and weighs 82 kg (180 lb); BMI is 23 kg/m2. Vital signs now are temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 120/min, respirations 22/min, and blood pressure 120/60 mm Hg. Physical examination is most likely to show which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
You are reviewing the results of a randomized trial in which 300 women with type 1 diabetes mellitus were selected to receive either a new oral hypoglycemic medication or standard therapy with insulin. By the end of the trial, 20 women taking the new oral hypoglycemic medication had discontinued the medication and switched back to their insulin regimen because of adverse effects of the new medication. However, statistical analysis was performed as if these patients had remained in the treatment arm. Which of the following best describes the type of statistical analysis that was performed in this randomized trial?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
A 6-month-old Asian girl is brought to the office by her mother because of diarrhea of 4 days’ duration, preceded by runny nose, fever, and vomiting. The mother tells you that her child’s stools initially occurred three to four times daily, but their frequency has increased to 12 daily for the past 2 days. The stools are dark green with no foul odor, blood, or mucus. The child’s vomiting subsided 2 days ago. Until the present illness, her diet consisted of cow milk formula with iron and prepared baby food. For the past 3 days her only intake has been over-the-counter pediatric electrolyte solution. She voided just before this visit. She weighs 6.3 kg (14 lb; 25th percentile) and is 64 cm (25 in; 25th percentile) long. Vital signs are temperature 38.0°C (100.4°F), pulse 120/min, respirations 30/min, and blood pressure 80/46 mm Hg. The infant appears to be alert. Anterior fontanel is not depressed or bulging. Eyes are not sunken and tears are present. Mucous membranes are moist. Skin turgor is good. Depression of the nail beds indicates capillary refill time is less than 2 seconds. Stools are green, free of mucus, and not foul-smelling. Stool tests negative for occult blood. At this time the most appropriate management is to prescribe which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
A 57-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a 5-day history of worsening malaise and fatigue. He reports that he tires when he walks more than two city blocks. Medical history is remarkable for poorly controlled hypertension. Medications include enalapril, clonidine, and hydrochlorothiazide. BMI is 28 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse 96/min, respirations 16/min, and blood pressure 208/111 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 98%. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination discloses a regular rhythm without murmur. Abdomen is soft and nontender. There is no lower extremity edema. Serum creatinine concentration is 3.2 mg/dL. Results of renal function studies obtained at an office visit 1 month ago were within the reference ranges. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
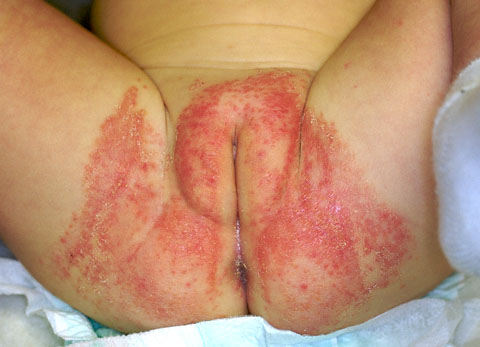
An 11-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department because of a persistent rash that began 2 weeks ago. The mother says she has been cleaning the rash with soap and water and over-the-counter products but has not noticed any improvement. The child’s medical history is unremarkable except for a period of vomiting and diarrhea that began 3 weeks ago and resolved after 5 days. Vaccinations are up-to-date. The child appears happy, is smiling, and is in no acute distress. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination discloses the rash shown. The rash blanches when pressure is applied. The most appropriate next step is to recommend which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
A 72-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 1-day history of shortness of breath, light-headedness, and an episode of near fainting. The patient also reports a 3-day history of dysuria, urinary frequency, and fever. Medical history is significant for osteoarthritis and hospitalization 3 months ago for elective right knee replacement. Her only routine medication is oxycodone. BMI is 20 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 39.0°C (102.2°F), pulse 130/min, respirations 28/min, and blood pressure 85/52 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on 100% oxygen by nonrebreather face mask shows an oxygen saturation of 94%. Initial physical examination shows bleeding from the site of previous phlebotomy attempts. Results of laboratory studies are shown:
Serum
Blood
Urea nitrogen
36 mg/dL
Hematocrit
30%
Creatinine
2.1 mg/dL
Hemoglobin
10.4 g/dL
Na+
140 mEq/L
WBC
16,000/mm3
K+
5.0 mEq/L
Platelet count
50,000/mm3
Cl−
100 mEq/L
PT
16 seconds
HCO3−
22 mEq/L
PTT
36 seconds
Plasma
D-dimer
600 μg/L (N<200)
Fibrinogen
80 mg/dL (N=200–400)
Urine
Leukocyte esterase
Positive
Nitrite
Positive
WBC
250/hpf
Bacteria
3+
In addition to intravenous 0.9% saline, which of the following is the most appropriate treatment to administer at this time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
A 56-year-old man, who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting with the mammary artery 3 months ago, is admitted to the hospital because of a 3-month history of recurrent episodes of unsteadiness and mild, spinning vertigo with walking. Within the first week following the operation, the patient developed episodic numbness of his left arm that initially occurred only during physical therapy. Now, exercise of his arms reproduces the tingling, unsteadiness, and vertigo. The symptoms resolve with rest. The patient is currently asymptomatic. Medical history is significant for coronary artery disease, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Medications are metoprolol, lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, 81-mg aspirin, and simvastatin. BMI is 27 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.8°C (100.0°F), pulse 68/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 145/75 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 98%. Physical examination shows well-healing surgical scars on the chest. The remainder of the examination, including neurologic examination, discloses no abnormalities. Results of which of the following studies are most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
A 65-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is admitted to the hospital because of a 1-week history of gradually worsening dyspnea, chest tightness, audible wheezing, and cough productive of yellow sputum. The patient was diagnosed with COPD 6 months ago during a hospital admission for similar symptoms; since that time, the patient has been readmitted on one occasion prior to today for an exacerbation of his COPD. Medical history otherwise is unremarkable. Routine medications are tiotropium bromide, budesonide, formoterol, albuterol as needed, and home oxygen therapy at 2 L/min via nasal cannula when ambulating. The patient smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 48 years but quit 6 months ago when he was diagnosed with COPD. BMI is 23 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 37.1°C (98.9°C), pulse 92/min, respirations 18/min, and blood pressure 138/84 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula shows an oxygen saturation of 93%. Auscultation of the lungs discloses diffuse wheezes bilaterally. The remainder of the physical examination discloses no abnormalities. Chest x-ray shows hyperinflation. The patient’s symptoms begin to improve after initiation of prednisone and moxifloxacin therapy. Which of the following therapies is most likely to improve this patient’s long-term survival?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
An 85-year-old man with early dementia, Alzheimer type, is brought to the office by his daughter for a routine examination. The patient lives alone in an apartment; a hired caregiver helps with bathing and dressing for 4 hours each morning. During the past month, his daughter, who lives 5 miles away, has had to go to his home several times each week in the evening because he has been confused. His daughter has been reading about the treatment of dementia, Alzheimer type, and asks the physician about vitamin E therapy for her father, which the physician knows little about. Which of the following is the most appropriate physician response?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
A researcher is conducting a study of a new drug to treat congestive heart failure. In preliminary testing, the drug has been shown to be effective in decreasing symptoms in 80% of patients, but 5% of the patients who take it develop venous thrombosis and, of those, 1% develop a pulmonary embolism. Which of the following approaches is most likely to be effective and ethical in recruiting potential study participants?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
A 60-year-old woman, who is recovering in the hospital 4 days after undergoing uncomplicated right hemicolectomy for cecal carcinoma, reports increasing shortness of breath during the past 6 hours. Medical history also is remarkable for type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, mild renal insufficiency, and myocardial infarction 4 years ago. Current medications are insulin, metoprolol, atorvastatin, and low-dose enoxaparin. She is receiving intravenous 5% dextrose in 0.45% saline. On admission, she weighed 113 kg (249 lb); BMI was 43 kg/m2. Weight today is 118 kg (260 lb); BMI is 45 kg/m2. Vital signs are temperature 38.0°C (100.4°F), pulse 130/min, respirations 20/min, and blood pressure 110/70 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on 5 L of oxygen via nasal cannula shows an oxygen saturation of 93%. Auscultation of the lungs discloses decreased breath sounds bilaterally. Heart rate is regular without murmurs; there is an S3 gallop. Abdomen is obese and mildly distended; bowel sounds are hypoactive. There is 2+ edema of the lower extremities bilaterally. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the findings in this patient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
A 60-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital because of nausea and vomiting. The patient reports anhedonia, anorexia, and anergy. During the exam, the patient tearfully says she misses her 77-year-old sister, who passed away 1 year ago. She says, “She was my best friend.” The patient is married. Vital signs are temperature 37.3°C (99.2°F), pulse 92/min and regular, respirations 20/min, and blood pressure 142/90 mm Hg. Neurologic examination discloses gait disturbance, downward gaze weakness, hypertonicity of the extremities, and bradykinesia. These findings are most consistent with which of the following?
CorrectIncorrect
